 |
Photo detection is the process of conversion from optical to
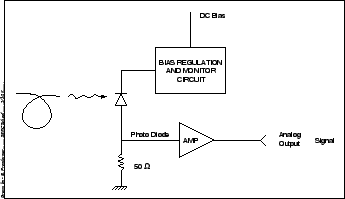
electrical domain. A block diagram of the GMRT optical receiver is shown
in Figure 22.6. The basic detector is a reverse biased p-n
junction diode. In this bias condition a reverse leakage current (the
dark current) flows. The threshold for detection is determined by
the dark current. The other important characteristic of a photo-detector
is its responsivity ![]() . The responsivity is a measure of the
efficiency with which light is converted to electrical current and it
is related to the width of the depletion region of the diode and to the
spectral response of the receiver. A larger depletion region leads to
a better responsivity. PIN diode detectors made of InGaAsP and grown
on InP are popular photo-detectors as they have low dark currents
and high responsivity. In the case of the GMRT, the detector used
has a dark current of 5 nA and
. The responsivity is a measure of the
efficiency with which light is converted to electrical current and it
is related to the width of the depletion region of the diode and to the
spectral response of the receiver. A larger depletion region leads to
a better responsivity. PIN diode detectors made of InGaAsP and grown
on InP are popular photo-detectors as they have low dark currents
and high responsivity. In the case of the GMRT, the detector used
has a dark current of 5 nA and ![]() of 0.8 mA/mW.
of 0.8 mA/mW.
In order to match the device to the electrical output device, care has to be taken to maintain a wide frequency response and to keep the thermal noise contribution of the detector low. In the case of the GMRT the laser noise is more than the thermal noise contribution of the photo-detector.